 |
|---|
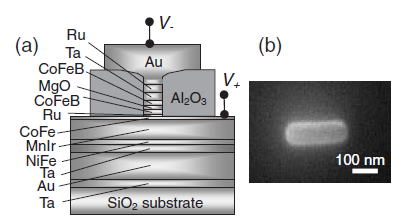
| Fig. 1 Schematic drawing of cross section of fabricated MTJ. The thickness of MgO is fixed to 0.85 nm. (b) Scanning electron microscopy image of a pillar after miling showing that the area of the fabricated pillar is 80 x 240 nm2 |
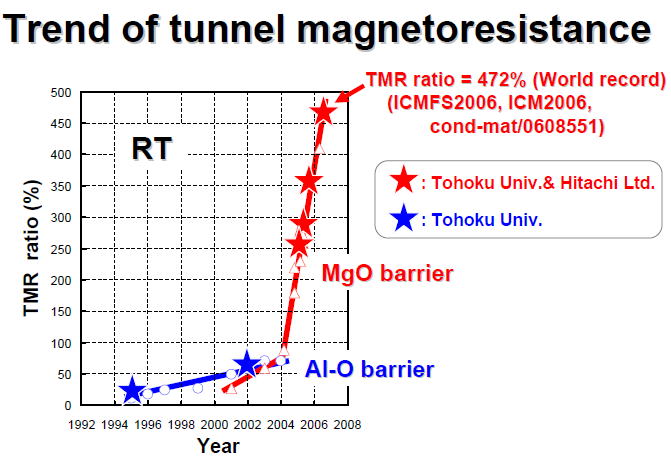 |
| Fig. 2 Thrend of tunnel magnetoresistance of MTJ. We have realized record tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR ratio =472 %) by using MgO-based MTJ. |
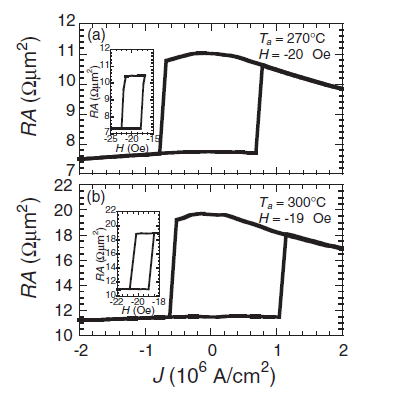 |
| Fig. 3 Resistance area (RA) product of versus current density (J) loops at room temperature for two samples annealed (a) at 270°C (sample A) (b) at 300°C (sample B). These curves were taken under a fixed external magnetic field to compenstate the effect of the offset field. The averaged critical current density is 7.8x105 A/cm2 for sample A and 8.8x105 A/cm2 for sample B. |